There are several supplements and other strategies that can markedly increase the success of oncology treatments for melanoma.
Research based on patient records reports strongly improved immunotherapy responses and lower progression risks with use of antihistamines, specifically H1 class such as loratadine. This effect is seen in other cancers, but is particularly in clear during treatment for melanoma. And well documented pre-clinical models describe how antihistamines re-regulate immune system behavior allowing oncology drugs to act on tumor cells. Histamine is identified as increasing risks for progression, a low histamine diet might be of use too. Also in immunotherapy responses, another study of case data crucially demonstrates that progression risks are more than halved for AM administration of immunotherapy vs PM https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4409/12/16/2068 Immune system behavior varies during the day, and here treatment response is much higher in the morning.
Sufficient and higher levels of vitamin D3 are also linked to much better immunotherapy treatment results and reduced risk of recurrence. As with many cancers, vitamin D3 deficiency is common in melanoma and should be corrected on a sustained basis. Studies of patient records have shown some strikingly large effects on progression in advanced stages, in those with higher vitamin D3 levels, and tendencies to lower risk for serious side effects too.
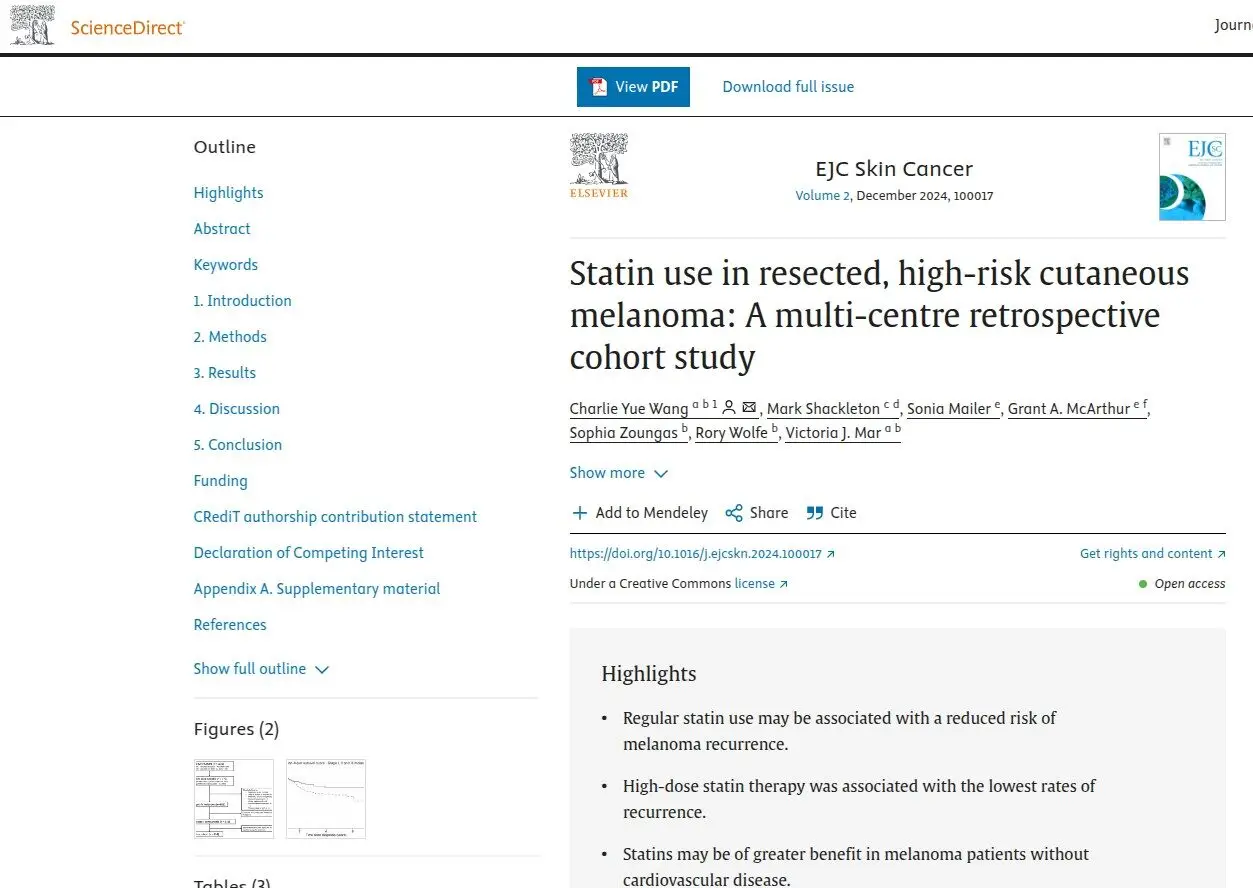
Similarly, large scale comparision of patient case data report that statin users have lower progression rates. Atorvastatin is the most widely researched, but when a prescription is lacking, well proven red yeast rice is a supplement equivalent. Its the source of lovastain, which interestingly can also help reduce “classic” systemic inflammation seen with so called CRP or c-reactive protein levels.
In patients that have relapsed from immunotherapy such as pembrolizumab (keytruda), significant numbers have benefitted from second round therapy when adding yeast derived beta glucans , getting more sustained responses. Also in immunotherapy, high dose aspirin is shown with improved outcomes for a sub-group of patients able to tolerate the dosages. Comparisons of patient records in melanoma also that even with low doses improve responses for earlier stage patients. Also in patent data, “responders” to immunotherapy have relatively higher levels of alpha ketoglutarate, now widely studied in anti-aging science. In melanoma there is very compelling evidence in lab study (mouse models) alongside the case data. Also crucial in reponse levels is a healthy gut microbiome with high bacteria diversity driven by fiber intake. Functional foods help this, and have their own anti-cancer mechanisms, such as walnuts. Along with these bacteria strains including akkermansia, the presence of inosine both natrually and supplemented has growing evidence of improving the response rates of immunotherapy. Significantly better responses are seen in case data for higher levels related to reduced treatment resistance.
Systemic inflammation is linked with increased risks for progression, especially in later stages. Both acute type inflammatory responses measured by C-reactive protein, and immune system related neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios. Maintaining relatively lower levels of both make a substantial difference. Commonly used Astragalus root has evidence of improving immune system balance and NLR while curcumin and other other functional foods including garlic can help bring down inflammation levels.
The so called Th1/Th2 immune system balance is strongly linked to the progression and to treatment resistance including in melanoma. Molecular iodine solutions are emerging in this area in breast cancer management and seen boosting Th1 anti tumor activity and helping suppress over active Th2 used in resistance. This has improved results in surgery plus chemotherapy and may support increased response immunotherapy (see Supplement Library)