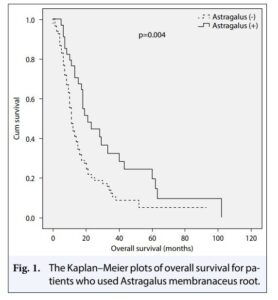
A meta analysis in 2010 analyzed the impacts of Astragalus extracts in a total of 65 clinical trials in china to map overall effects. 4751 lung cancer patients received Astragalus extract alongside standard chemotherapy and oncology treatments. The study finds a 6 month decrease in risk levels of 46%, with lower but significant 35% and 26% at the one and two year time periods. For the first year of treatment, Astragalus decrease the risks of treatment failure by 35% after a year, and still at 35% after 2 years. The tumor response rates, meaning measurable improvements in tumor size, across 27 trials, were 43% higher likelihood of the most significant reductions , and also 35% higher of at least partial effects on tumor burden indicating probable overall quality of life benefits.
These trials showed much the same results, indicating consistent findings despite differing quality levels. That said, there are trials finding no effect published and included in the data, and the researchers find no evidence of bias. There results are more than those found from adding immunotherapy drugs to chemotherapy.