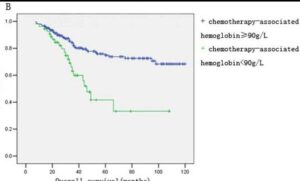
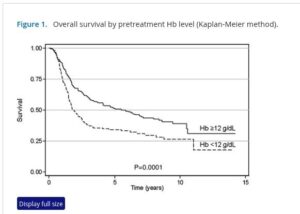
A well balanced iron metabolism is crucial to results from modern targeted treatments. Good hemoglobin is an independent marker of successful outcomes in immunotherapy There is growing evidence in chemotherapy too, which strongly depresses hemoglobin levels. Evidence in lung cancer reports over 2X better response even at the already low cut off of 110g/dL level (see References). As a side note the reported risk reductions are about a half for those with combination therapy of immunotherapy plus chemotherapy. So the group with combination therapy and good hemoglobin saw radically improved results. Similarly in breast cancer studies show more than 2X benefit to good hemogloblin.
Time after time, studies confirm that inflammatory like iron states or “iron overload” are common during cancer and strongly linked to progression. But iron deficiency is equally damaging, and is present in up to half of patients at diagnosis and the vast majority once oncology treatments start. Lactoferrin is a milk protein compound similar to bovine colostrum, but without unnecessary growth factors and hormones. Through its supportive effects on microbiome, it is classed as a prebiotic and shows protective effects on immune system health in colorectal cancer during oncology. Its biological impacts include helping to connect innate and adaptive immune response. And at least one trial with advanced stage lung cancers reported tendency to lowered progression rates. A few cases are reported in pilot studies with lactoferrin in metastatic kidney cancer with greatly extended disease free periods for about a quarter of patients (see Examples).
Many cancers upregulate availability of iron for their growth and spread, storing it locally for use as enzyme like proteins called ferritin which can be seen in circulation. At the same time, this can contribute to iron deficiency or even anemia, with is commonly reported at diagnosis and may increase during treatment. Low iron a well known factor in metastatic spread of cancer, and a risk factor for both progression and and side effects. Lactoferrin strongly binds iron in the gut, and regulates its absorption. This can re-balance iron, help fight cancers iron related activity including reducing inflammation and stabilzing ferritin levels. This process is helped immensely by a diverse and healthy microbiome.
Actions on the microbiome also help correct the metabolism of cysteine and methionine. These amino acids play significant roles in several aggressive cancer types, including TNBC, myeloma, melanoma, ovarian and liver cancer, lactoferrin at moderate levels may partly support targeted dietary regimes to reduce these amino acids. (see also Soy in the Foods Library)
Immune system activation from lactoferrin restrains the growth of colon polyps reducing risks they will become pre-cancerous (see References). In terms of boosting innate immunity and reducing inflammation, a number of studies, not all, show both anti-inflammatory and immune regulating effects. For instance in reducing levels of IL-6, and in some studies c-reactive proteins. And in other research lactoferrin has shown effects associated with boosting of natural immune activity through T-cell activation (see Highlights). A study in colorectal cancer patients showed strong reductions in key biomarkers of disease activity and progression, including Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
There is compelling pre-clinical evidence that the presence of lactoferrin reduces key steps in cancer metastasis, but this requires some additional evidence in relation to patient trials. A lysosomal formulation is an option to increase bioavailability. Start lactoferrin before oncology treatments if possible, to help balance iron levels and reduce tumor access to its preferred ferritin form.