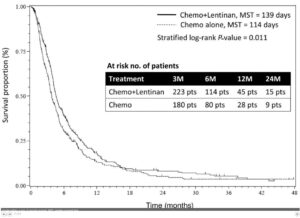
In Japanese oncology, mushroom extracts including turkey tail (PSK) and shitakke (lentinan) have a long track record. Mushroom and yeast based beta glucan 1,3/1,6 are now sources for emerging branded products too. Also from asian oncology, analysis across multiple clinical trials concludes that astragalus root extract also reduces relative risks, and improve side effects. Astragalus can re-balance immune related inflammatory responses, so called neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios. This inflammation often flares up due to treatments or disease progression.
Research on statin use in gastric cancer has varied findings, but a recent national scale study in Tiawan explains some of this. And finds that there are risk reductions that increase with use over time. In other cancers, results show its “responders” to cholestrol control that see large benefits. Also with somewhat mixed research results in gastric cancer, vitamin D3 , results in a recent trial named AMATERASU headlines with no effects. But a detailed look at that data clearly shows tendencies to reduce progression, and much more so in older patients, male and early phase.
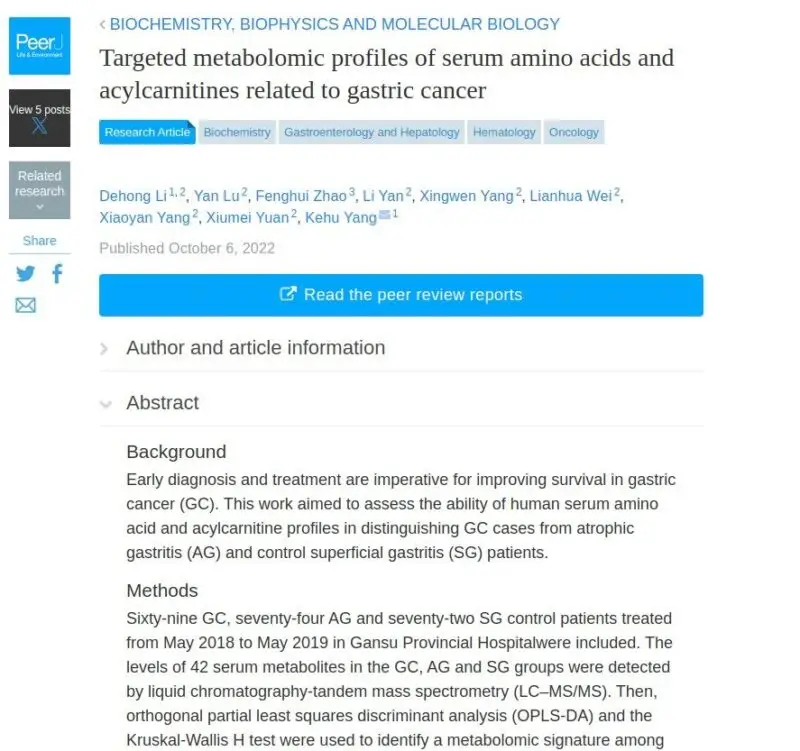
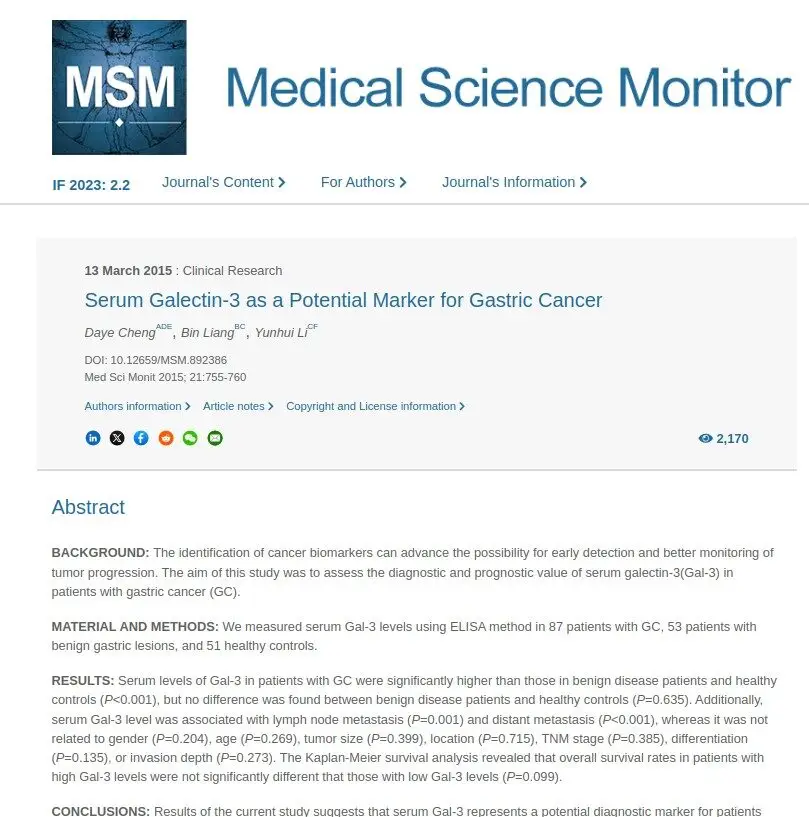
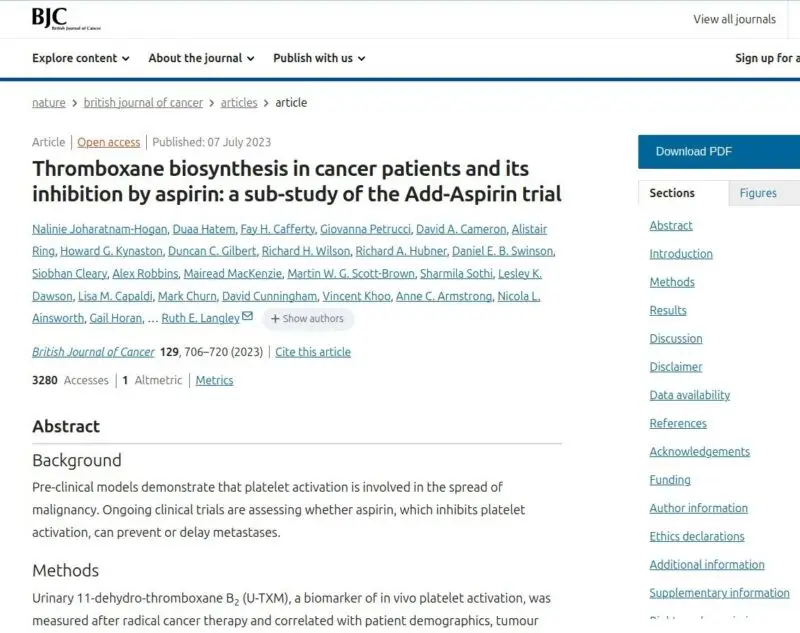
A prebiotic in anti-aging science, lactoferrin, is found to significantly improve side effects of chemotherapy. And, fascinatingly, it drives strong reductions in key biomarkers of disease activity and progression such as carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) seen in 90% of gastric cancer patients. Lactoferrin is a strong regulator of iron absorption, and its actions can help decrease anemia which is very common in gastric cancers, and predicts poor response rates to treatments, especially immunotherapy. But in the opposite direction, it can help bring excess stored iron in the tumor regions (“ferrtin”) back to normal ranges. High iron in the tumor regions or circulating as ferritin also worsens oncology outcomes and increases risk. Perhaps an even bigger driver of progression are studies showing elevated platelet levels from upregulated “clotting” thromboxanxe enzymes, which are strikingly elevated in gastric cancers. These increase metastatic spread rates. A sub study of the ADD-ASPIRIN ongoing trial shows effective suppression of thomboxane at low dose level.
Citrus Pectin has ongoing trials in oncology, even patented drug development targeting the same mechanisms. There are results showing some benefits in treatment, and importantly good evidence in case studies that citrus pectin can bind toxic heavy metals. Copper is usually elevated by digestive system cancer to increase its growth, higher levels are reported to very strongly increase progression risk. Another typical dysregulation are higher levels of circulating fatty acids to drive growth of gastric cancer. In anti-aging trials, Urolithin A supplementation could help improve metabolism of these compounds.
Vitamin B3 supplementation during treatment for digestive cancers has been shown to extend survival rates in case history data. More specific to gastric cancer, new research has also shown improved outcomes with K3 supplementation https://www.annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-7534(24)03015-1/fulltext . Dysregulated metabolism of amino acid tryptophan is shown increasing gastric cancer patient progression. In sports science, regulation of tryptophan metabolism by gut microobe akkermansia with lactate (eg yoghurt) can help promote healthy tryptophan absorption.
Systemic inflammation has been shown to substantially increase risk of progression. Curcumin is a useful anti-inflammatory supplement, as is garlic while pro-inflammatory diets are similarly found to be negative in case records. The inflammatory response seen in immune system markers may equally be helped by beta glucans.
The so called Th1/Th2 immune system balance is strongly linked to the progression and to treatment resistance. Molecular iodine solutions are emerging in this area in breast cancer management and seen boosting Th1 anti tumor activity and helping suppress over active Th2 used in resistance. The has improved results in surgery plus chemotherapy and may support increased response immunotherapy (see Supplement Library). For immunotherapy the presence of high sodium levels is now identfied as a key marker for success in other cancers. Also in other cancers, AM treatment programs are substantially more effective that PM/evening sessions
Liver is the most common metastatic site, it may be useful to take a look for inspiration in that Pathfinder too. There is some compelling indirect evidence that luteolin can reduce metastatic activity too, something to consider in both dietary and supplement regimes.