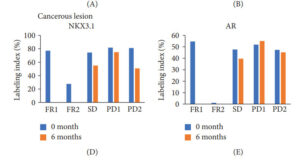
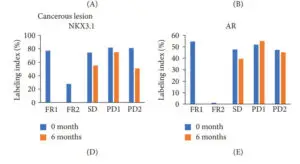
A recent pilot study in five patients in early phase prostate cancer and PSA below 15ng/L. With both non cancerous and cancerous lesions, 4 were initally judged low and 1 intermediate risk. During active surveillance, luteolin was adminstered at a low dose, only 50mg daily for 6 months. This amount is only 4 to 5oz of radicco. Even so there were promising effects reported here.
Two patients showed clear responses, and one achieved stable disease. These actions include both reduction in so called Androgen Receptor activity levels, and increased molecules identified as miR-29 and miR-30, often seen acting as tumor suppressors. In one patient, the report includes complete disappearence of a cancerous lesion, remarkable to say the least and at low dose. No side effects were detected and its probable that at least some or even all of these anti-cancer actions are dose dependent. The data below clearly shows that responders had androgen receptor activity suppressed with luteolin.
The androgen receptor targeting drug enzalutamide operates in a similar way. Luteolin has no reported side effects, in fact its likely to have other positive effects.