Comparing thousands of cases across Scandinavia has shown lower progression risk in users of antihistamines especially loratadine. Similarly, patient studies for vitamin D3 levels and outcomes confirm the advantages in having relatively high levels. Vitamin D3 deficiency is common in many cancers including ovarian, and is reported to be a marker for worsened prognosis. Also from case data, use of low dose aspirin has its highest impact in post-diagnosis users, increasing progression free time and, importantly, reducing all cause risk even in advanced stages. The researchers make the comparision with result of adding an immunotherapy drug to the chemotherapy treatment. Its apparent that during stages I to III, low dose aspirin has by far the larger impact in slowing down progression.
Aspirin can also amplify the actions of statins, and the latter are also shown from patient data to measurably improve the prognosis with post-diagnostic use. Increased cholesterol activity is one common finding in how many cancers can grow and progress. Comparing users to non users in studies has shown lowered risks for progression in ovarian cancer management. Where a prescription for something like atorvastatin is not available, the well proven supplement red yeast rice is the natural source of lovastatin. There are several oncology drug classes often increasing lipid levels, so sustained use is beneficial. Effects are often reported as highest in those who respond with lower LDL levels.
New research in Sweden shows strongly elevated levels of so called gal-3 inflammatory proteins at both local and metastatic sites. The study shows how natural immune response is turned off in a third of patients. This recent finding links with evidence that responders to citrus pectin therapy, about a quarter to half of patients respond positively. Importantly, citrus pectin especially combined with marine alginates has been reported to remove heavy metals. Studies implicate high serum copper as a factor in progression rate. During a recurrence phase, researchers have also reported a large drop in zinc levels. The mechanisms behind this include cancer switching immune system activity to allow its growth. So far there are no trials to show effects of supplementation. Healthy pre-diagnostic zinc-selenium levels are strongly linked with better outcomes in several cancers, and now high dose selenium within oncology has shown some striking results. These include a pilot trial in advanced ovarian cancers where up to a quarter of patients showed sustained progression free responses with chemotherapy.
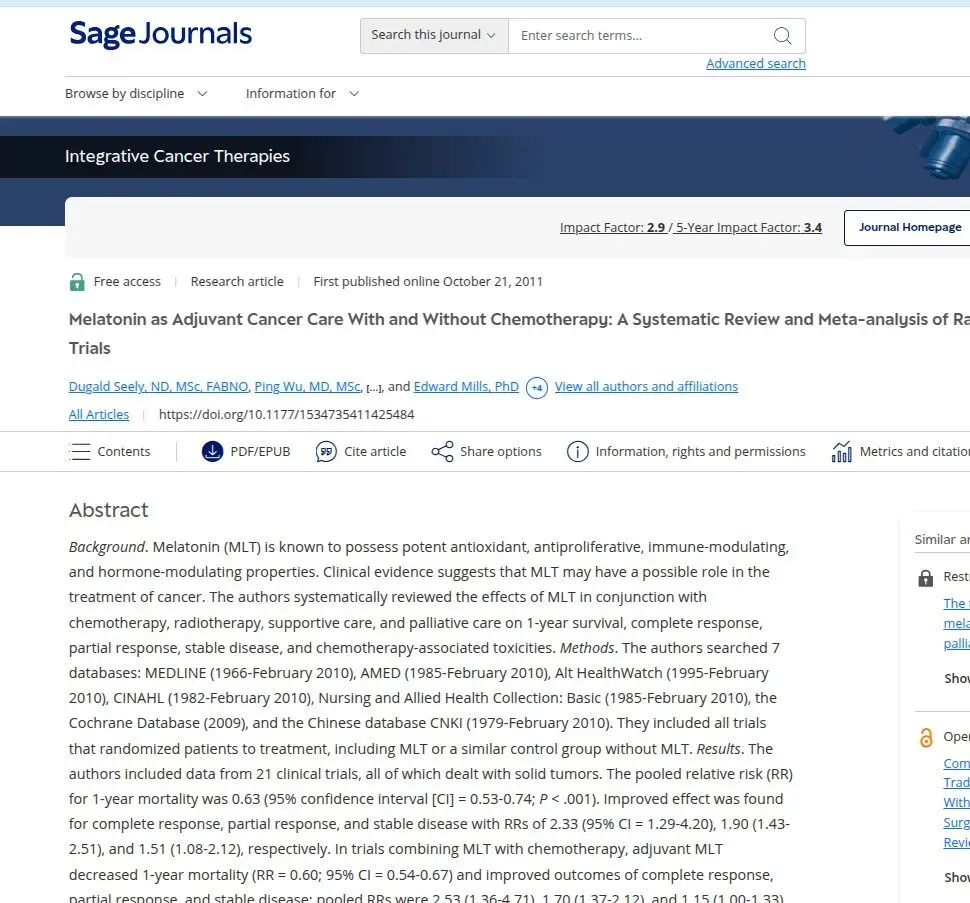
A crucial hormone for whole body health, melatonin is frequently very depressed in a variety of cancer patients at diagnosis not least ovarian. Even at very late stages, some patients across multiple disease types respond to moderate to high dose melatonin with boh stable disease and improved quality of life.
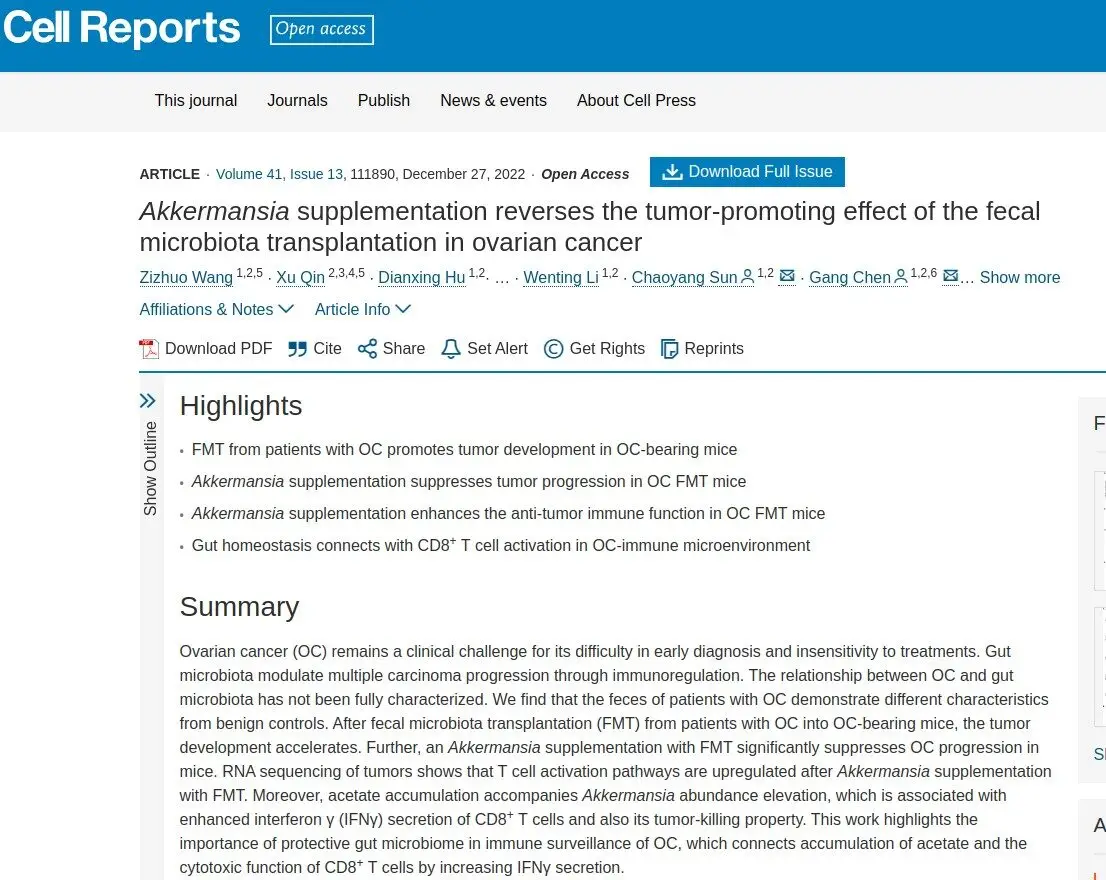
Having a diverse healthy gut microbiota is a driver of lower risk and better treatment results. Studies find the bacteria strain called akkermansia is deficient in ovarian cancer limiting immune response to cancer. Akkermansia with lactate (e.g probiotic yoghurt) can also help regulate metabolism of tryptophan, and amino acid linked to high progression risk when dysregulated by ovarian cancer to fuel growth. Functional foods such as nut consumption increase levels of akkermansia and and many other beneficial bacteria strains. In dietary interventions there are current ongoing trials with crushed flaxseed also, which can act help balance hormone levels and improve microbiome at the same time.
Systemic inflammation is linked with increased risks for progression, especially in later stages. Both acute type inflammatory responses (measured by c-reactive protein or CRP), and immune system related inflammation (NLR or neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios). Maintaining relatively lower levels of both make a substantial difference. Commonly used Astragalus root has evidence of improving immune system balance and NLR while curcumin and other other functional foods including garlic can help bring down systemic inflammation (and so lower CRP).
The so called Th1/Th2 immune system balance is strongly linked to the progression and to treatment resistance. Molecular iodine solutions are emerging in this area in breast cancer management and seen boosting Th1 anti tumor activity and helping suppress over active Th2 used in resistance. The has improved results in surgery plus chemotherapy and may support increased response immunotherapy (see Supplement Library). For immunotherapy the presence of high sodium levels is now identfied as a key marker for success in other cancers. Also in other cancers, AM treatment programs are substantially more effective that PM/evening sessions