Multiple supplements and functional foods have strong direct or indirect evidence of improving TNBC treatment results. A few differ from hormone driven tumor types. Overall the mechanisms frequently include improving anti tumor immune response, reducing treatment resistance and balancing both inflammation and levels of crucial minerals and vitamins.
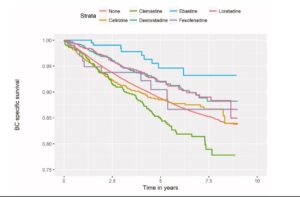
Much lower risks for progression in TNBC are reported in post-diagnosis statin users, particularly those under active surveillance for elevated blood cholesterol levels. Cholesterol “responders” have been identified as benefiting from statins in studies of other cancers. Where a prescription statin is unavailable, red yeast rice is the natural source of lovastatin while atorvastatin is perhaps the most researched otherwise. In this research, the effects were even greater at higher doses.
National scale patient records studies report vitamin D3 levels affect outcomes, where deficiencies are common in most cancers. Higher levels are linked with improved response to pre-surgery chemotherapy and reduced risk of disease progression. These findings indicate the potential importance of maintaining sufficient vitamin D3 levels during TNBC treatment, interventional trials are now starting up employing 50,000IU weekly dose for 20 weeks along with chemotherapy (oral form, cholecalciferol).
Patient data also shows that increased levels of circulating enterolactones, high in crushed flax seeds, significantly lowered all cause risks in ER negative patient groups. As much or more than in ER positive types, perhaps unexpectedly so. Equivalent research into low dose aspirin has varied findings, but the weight of evidence for use of anti-platelet compounds is positive, including for reducing metastatic activity. Diet related, lifestyle changes can impact recurrence and risk levels quite substantially. Both anti-inflammatory diets and structured exercise are increasingly reported to improve outcomes. Interestingly, TNBC outcomes were especially improved by a fasting mimicking diet during treatment in a larger multi-cancer trial, which is suggested to be due to increased immune system activity over time (see Lifestyle)
The so called Th1/Th2 immune system balance is strongly linked to the progression and to treatment resistance. Molecular iodine solutions are emerging in this area in breast cancer management and seen boosting Th1 anti tumor activity and helping suppress over active Th2 used in resistance. The has improved results in surgery plus chemotherapy especially in stage III, and may support increased response immunotherapy (see Supplement Library). For immunotherapy the presence of high sodium levels is now idenfied as a key marker for success in other cancers. Also in other cancers, AM treatment programs are substantially more effective that PM/evening sessions
Higher levels of anti-aging supplement alphaketoglutarate have also been linked to immunotherapy response levels in several cancer types. Some fascinating lab studies (mouse models) have shown dramatically increased success for radiotherapy in TNBC. This widely studied anti-aging supplement has increasing preclinical evidence for its use alongside oncology drugs. Also related to much improved immunotherapy outcomes, a branded beta glucan product showed remarkable effect in metastatic, relapsed, TNBC patients with pembrolizumab (Keytruda). These immune enhancing compounds have expanding numbers trials, and similar yeast derived beta glucans are commercially available.
Also common in TNBC especially african american women are low levels of melatonin receptors, leading to much increased risks of progression. Whilst specific trials are lacking, advanced stage patients including breast cancers have, in some cases, seen substantial benefits (see Supplements Library). Melatonin is now being studied at up to 1g per day with some fascinating results published. Less well known are the surprising effects of functional foods based on oats and eggs that stimulate anti-inflammatory responses able to counter fluid pressure in tumors, pressure that drives not only growth and metastatic spread, but also drug resistance
As it progresses, breast cancer often upregulates availablity of iron to fuel growth shown by levels of the protein ferritin. Low levels are linked with improved prognosis, whilst increasing levels are seen with metastasis, particularly to the liver. Conversely, iron deficiency is common and increases during therapy, linked with much higher progression risks. The pre-biotic milk protein lactoferrin binds iron in the gut and regulates iron balance, homeostasis, and has its own evidence for anti-cancer activity. The same study highlights the benefits of lowering systemic inflammation c-reactive protein (CRP), indicating the importance of anti-inflammatory supplements and functional food diets.
High serum levels of copper especially with insufficient selenium and zinc are linked with poor prognosis.The exact mechanism is still being clarified, but one possibility is cancer switches the metabolism to free up copper for its needs to grow and spread rapidly, and down regulates selenium. Heavy metal detoxification has been shown in patient case with use of citrus pectin, ideally with marine alginates. In kidney cancer, high dose selenium has been shown to allow oncology drugs to penetrate tumors much more effectively, and has ongoing clinical studies. Citrus pectin has its own distinct anti-cancer mechanism, inhibiting the galectin-3 protein signaling which is a factor in nearly 2/3 of TNBC tumors growth and spread.
Systemic inflammation is linked with increased risks for progression, especially in later stages. Both acute type inflammatory responses measured by C-reactive protein, and immune system related neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios. Maintaining relatively lower levels of both make a substantial difference. Commonly used astragalus root has evidence of improving immune system balance and NLR while curcumin and other other functional foods including garlic can help bring down CRP. Widely used herbal extract astragalus has detailed lab studies showing its improvement in oncology drug results, with supporting TNBC patient records on improved outcomes. Also related to immune system balance, there is new research reporting large effects in maximizing chemotherapy outcomes in patients with relatively higher selenium levels. Similar to studies in across all types of breast cancer patient data, but amplified in TNBC for yet unknown reasons.
In repurposed drug trials, the combination of etodolac and propranolol is showing promise (see Repurposed Drugs)