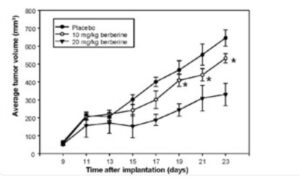
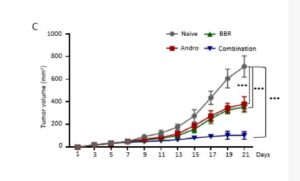
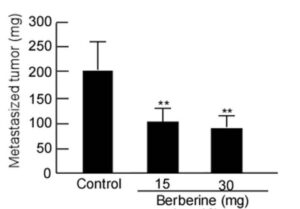
A naturally occuring compound in several plant species including barberry, goldenseal and more. Berberine effectively reduces insulin resistance in the level of prescription drugs like metformin, but unlike metformin has never been shown to have negative effects in cancer outcomes. It is certainly the case that reducing insulin resistance has a protective effect in terms of cancer risk, whilst research studies to support that rely on users of metformin. Other reports have successfully combined berberine with metformin and statins to increase impacts. And with other supplements such as red yeast rice too in metabolic disorders , including branded supplments such as Berberol K. (see References)
Insulin resistance leads to elevated blood glucose levels, frequently shown to increase the incidence and spread of tumors. Studies demonstrate its negative impacts in several cancers. Most prominently colorectal, liver, lung, pancreatic, head and neck, and postmenopausal breast cancers. And probable links with gastric, clear cell kidney. Though evidence is mixed for prostate cancer, and non-existent for melanoma, glioma, lymphoma.
Its anti-bacterial actions and support of a health micro-biome contribute to results in some trials showing protection benefits during radiotherapy. There is evidence in clinical trials that berberine reduces recurrence of benign colorectal polyps following surgery, from around a half to around a third of patients. And a trial on berberine chloride to reduce incidence of colorectal cancer in patients having ulcerative colitis. One action proposed is the reduction in a cancer driving bacteria in the gut veillonella parvula
A small trial showed protective effects during radiotherapy. Additionally, berberine has shown strong anti-inflammatory actions inluding reductions of c-reactive proteins and IL-6. And, int the moderation of lipid metabolism, so called fatty acids. Even in reduction of hormone growth factors including leptin. All of these are separately associated with increased progression in various cancers, and all may benefit from reducted activity in the presence of berberine. Effects can take a week or two to materialize.
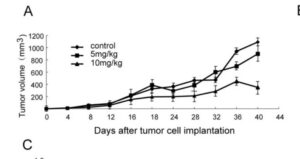
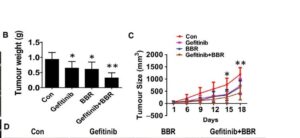
There are a lot of pre-clinical reports of anti-metastatic effects, though these need more evidence from cancer trials. Whilst absorption is limited, the reality shows its enough and any good quality brand will drive these effects.