Research based on patient case data for antihistamine effects shows positive impacts for Hodgkin lymphomas – use of desloratadine leads to much lower risks of progression, specifically in the Hodgkin variant. Similar study of patient records in other cancers confirms superior response rates during immunotherapy, which researchers suggest are also applicable to lymphoma.
The substantial positive impacts found for higher levels of vitamin D3 include an interventional trial that was able to correct levels of this crucial compound in about a quarter of patients. The effects include over 60% improved event free survival during immunotherapy. This would be a much larger effect if comparing full normal levels with clearly deficient patients.
Beta glucans derived from mushrooms or yeast, both commercially available and proprietary forms, are increasingly shown to support oncology treatments including lymphomas. Evidence includes increasing treatment response rates and improving and balancing immune system activity. Re-balancing immune system inflammation levels, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and improving low platelet count both reduce risks quite substantially. Along similar lines the well proven herbal supplement, astragalus, is a natural immune modulator with evidence for rebalancing immune system related inflammation. This may help treatment response, and also potentially lower its side effects.
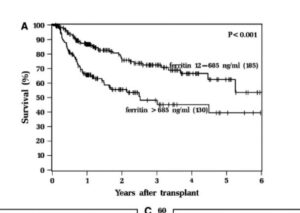
Abnormally high circulating iron in the form of an enzyme like protein called ferritin are closely linked to poor prognosis. Cancers can use ferritin to store iron needed to fuel growth requirements. However, low iron or even anemia is also a big risk found in patient data. The prebiotic classed supplement lactoferrin can counteract the cancer related iron activity, it binds iron in the gut and drives healthy metabolism and balance – so called homestasis. Well balanced ferritin and iron predict much more sustained treatment responses.
Treatment outcomes in lymphomas are heavily influenced by gut microbiome. A high diversity of gut bacteria is reported to improve stem cell therapy success and slowing of progression. Crucially, therapy failure is linked to poor gut microbiota and in particular deficiency or even absence of blautia and akkermansia bacteria. Some necessary oncology treatments reduce levels of these bacteria as do antibiotics.
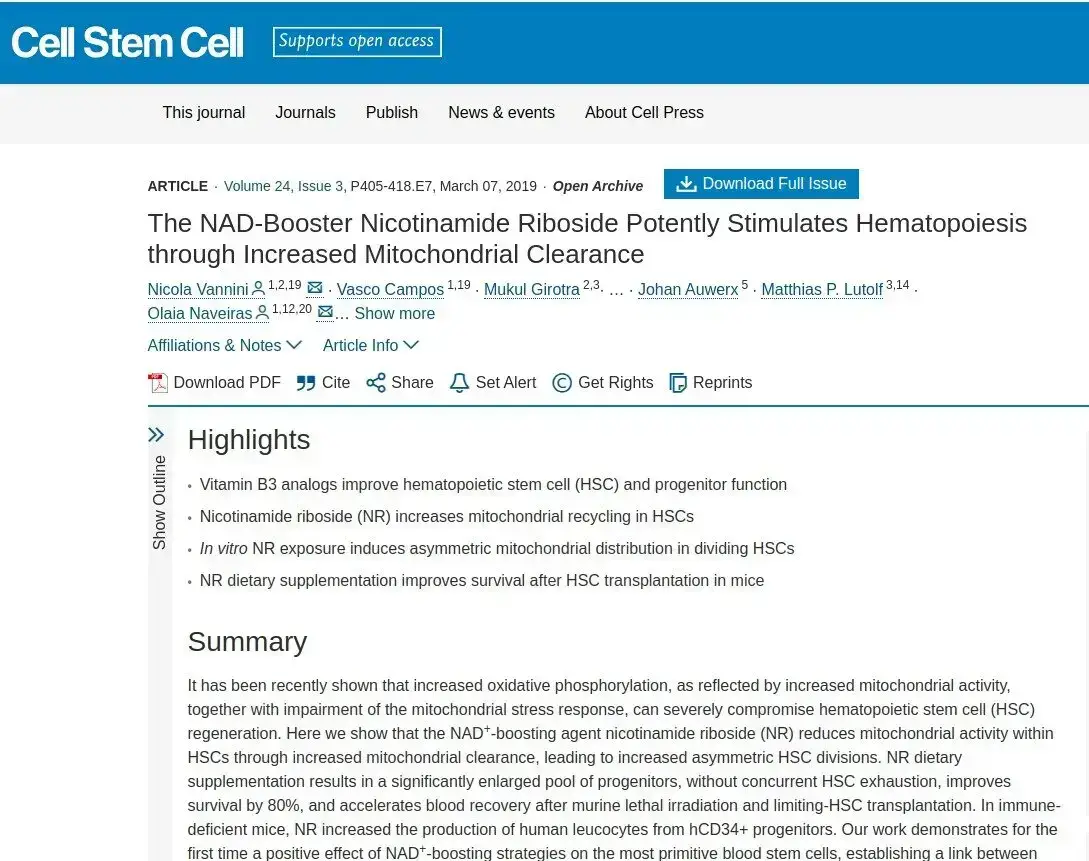
Successful treatment relies strongly on how quickly new white blood cells can be produced. The Nicotinamide Riboside variant of vitamin B3 has been extensively studied in anti-aging science for its ability to increase cellular mitochondrial health. Now, there are is remarkable pre-clinical evidence that this vitamin can substantially increase stem cell activity that drives production of new white blood cells. Related, another form of B3 has reached phase II for reducing incidence of melanoma in lymphoma and leukemia patients.
A commonly available anti aging supplement, alpha-ketoglutarate, is emerging as a potential supporting role during immunotherapy. Patient data including in lymphoma shows higher levels of responses with increasing levels of AKG, and highly compelling lab studies have confirmed the likely metabolic effects that improve drug activity.
Systemic acute type inflammation is associated with most cancers and resistance to treatment. Supplements including curcumin, garlic and an anti-inflammatory functional food regime are all evidence based interventions, often reported as lowering so called c-reactive protein levels (CRP).
The so called Th1/Th2 immune system balance is strongly linked to the progression of lymphomas and to treatment resistance. Molecular iodine solutions are emerging in this area in breast cancer management, seen boosting Th1 anti tumor activity and helping suppress over active Th2 used in resistance. This has improved results in surgery plus chemotherapy and may support increased responses during immunotherapy (see Supplement Library). For immunotherapy the presence of high sodium levels is now identfied as a key marker for success in other cancers. Also in other cancers, AM treatment programs are substantially more effective that PM/evening sessions