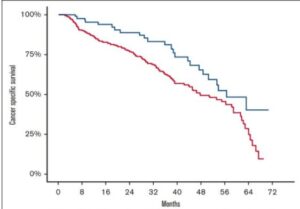
Treatment outcomes in lymphomas are heavily influenced by gut microbiota and the range and types of bacteria strains. Comparing patient case data has reported on how high diversity of gut bacteria improves stem cell therapy success results including reduced overall risks. Crucially, therapy failure is linked to poor gut microbiota and in particular deficiency or absence of blautia and akkermansia bacteria types. Some necessary oncology treatments reduce levels of these bacteria as do antibiotics.
Recent strudies have reported large advantages in having higher levels of vitamin D3. An active supplementation trial in Hodgkin Lymphoma was able to correct D3 levels in about a quarter of patients, and reports over 60% improved recurrence free response during rituximab immunotherapy. This would be a much larger effect if comparing full normal levels with clearly deficient patients. Mechanisms around vitamin D3 differ slightly in Non Hodgkin but these studies are highly relevant.
Also with rituximab, significant numbers of previously and refractory treated patients have benefitted when yeast derived beta glucans have been added in oncology increasing the response rate to oncology drugs and increasing immune system activity in patients. Whilst these trials can be with patented compounds, many of the effects reported have also been seen in 1,3/1,6 beta glucan supplements. Successful treatment for lymphomas relies strongly on how quickly new white blood cells can be produced. The Nicotinamide Riboside variant of vitamin B3 has been extensively studied in anti-aging science for its ability to increase cellular mitochondrial health. Now, there are is remarkable pre-clinical evidence that this vitamin can substantially increase stem cell activity that drives production of new white blood cells. Related, nicotinamide B3 has reached phase II for reducing incidence of melanoma in leukemia patients.
Systemic acute type inflammation is associated with most cancers, and often measured with c-reactive protein. Supplements including curcumin, garlic and an anti-inflammatory functional food regime are all evidence based interventions. Re-balancing immune system inflammation levels, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and improving low platelet count both reduce risks quite substantially. A natrual immune modulator, Astragalus has evidence of supporting both before and during oncology treatments.
The so called Th1/Th2 immune system balance is strongly linked to the progression in NHL and to treatment resistance. Molecular iodine solutions are emerging in this area in breast cancer management, seen boosting Th1 anti tumor activity and helping suppress over active Th2 used in resistance. This has improved results in surgery plus chemotherapy and may support increased responses during immunotherapy (see Supplement Library). For immunotherapy the presence of high sodium levels is now identfied as a key marker for success in other cancers. Inosine has also been linked to better outcomes. Also in other cancers, AM treatment programs are substantially more effective that PM/evening sessions
For non hodgkin patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as ibrutinib, a 2025 large analysis across nearly 1500 cases showed that stain use confers a risk reduction of over 60%. Its to be proven if this effect would be seen in the other 71% of patients who were not on statins, or a sub group of those. But a remarkable effect none the less.