Known for its role in thyroid health and association to wakame and other seaweeds. Well balanced levels of iodine are needed by the immune system. Marine sources also contain the so called molecular I2 form of iodine, as well as the “regular” type, and are often associated with lower cancer incidence in population studies in Japan, where for instance prostate cancer rates are only about 1/4 of those in western countries. Other metals from marine sources such as copper are negatively indicated in cancer development, so in dietary sources some moderation is indicated.
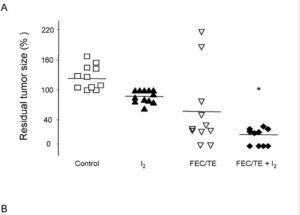
There is recent research on readily available molecular I2 iodine solution supplements in post surgery setting for breast cancers. Results confirmed promising pre-clinical results. Molecular iodine both exhibits direct suppression of cancer, and works effectively alongside first line chemotherapies to lengthen progression free periods and lower recurrence rates (see Examples). These study requires confirmation, but clearly show early potential for post-diagnostic use. Supporting this are similar improved outcomes using iodine solution forms in pre-emptive , preventative, surgery in high risk BRCA-1 carrying women. And, clinical trials in a third setting demonstrated that 5mg daily could notably increase innate immune response activity in breast cancer patients.
The proposed mechanism by which molecular iodine solutions support chemotherapy results involve regulation of the so called Th1/Th2 immune reponse. Iodine is shown boosting the tumor immune response by activating Th1 responses. But also damping the Th2 “allergy like” immune system activity, cancers use this upregulated “Th2”, to resist treatment actions of drugs. Its quite likely the same Th1/Th2 effects of iodine would help improve immunotherapy results. As well as breast cancer, many or even most cancers are linked to abnormal Th1/Th2 status. Including gynecologic and hematologic, gastric, head and neck, and prostate cancers.
Some , not all. studies show evidence that dietary iodine levels have preventative actions in breast, gastric, prostate and other cancers. Reseachers have proposed iodine deficiency in young women as a driver of rising rates of metastatic breast cancers, linked with low thyroid function. Iodine also works in synergy with selenium, and this may also affect how clearly studies are able to link these two compounds when investigated separately. For prevention, dietary sources are recommended in studies, not supplements.
There are commercial product ambitions for preventing and treating non-cancerous benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), based on evidence from population studies lab work. In men with BPH, research shows 5 mg daily of Lugol’s solution improved major symptoms in a few months.