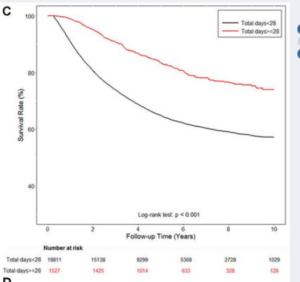
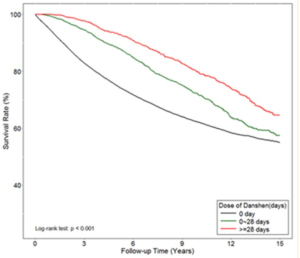
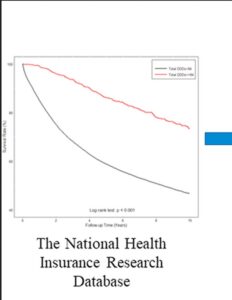
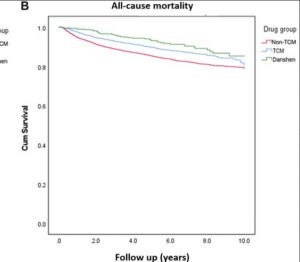
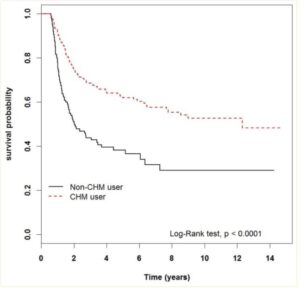
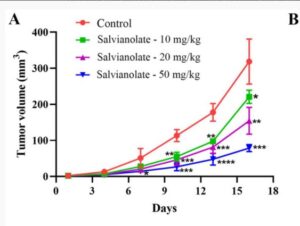
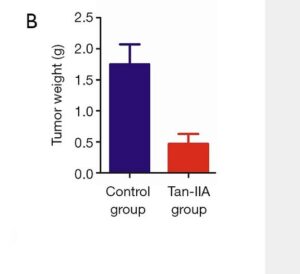
This large scale analysis on 40,000 patients with advanced prostate cancers in the Tiawan national health database 1997 – 2012. Data shows very significant medium and even long term survival increases from adding danshen to a variety of androgen deprivation treatments, particularly for doses at 3g daily longer than a month -measured because that means more than one prescription was taken out. Danshen has effects both for androgen dependent and independent prostate cancers.
The long term survival over a 15 year time span shows the sustained users of 3 x 1g per day demonstrate approximately 10 percent absolute improvement in 15 year survival probability. Medium term the improved survival rates were even higher, at 7 years the data shows more like an absolute decrease in risk of 15 to 20 percentage points If correct, this is comparable to or better than the newest oncology drugs such as enzalutamide https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0302283820303298
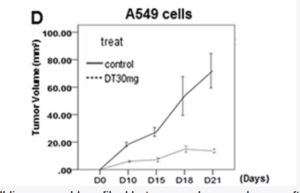
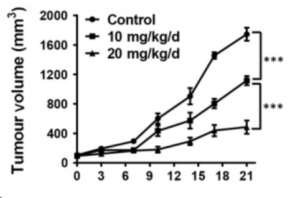
The study includes lab work on how danshen adds to androgen deprivation therapy by inhibiting the CCL2/ STAT3 signaling pathway. This process is heavily used by prostate cancer to grow and spread, by switching white blood cells in the immune environment in its favor. Increased STAT3 metabolic signaling is a driver of most major cancers growth and the metastatic process: prostate, breast, kidney cancer and many more.